The upright bike is a popular exercise machine. It provides a low-impact workout.
But what muscles does the upright bike work? Riding an upright bike targets multiple muscle groups. It mainly works your legs, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves. The workout also engages your core muscles and glutes. This makes it a great option for a full-body exercise.
Whether you’re a fitness beginner or a seasoned athlete, understanding the muscles engaged can help you maximize your workout. In this blog post, we will explore the specific muscles worked by the upright bike and how it benefits your overall fitness. Ready to learn more? Let’s explore!
Table of Contents
Upright Bikes
Upright bikes engage multiple muscle groups. They primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves. Additionally, the core and glutes also get a good workout.
Upright bikes are popular in gyms and homes. They offer a great cardio workout. These bikes resemble regular bicycles. You sit upright while pedaling. This position engages various muscle groups.
Brief History
The upright bike has a rich history. It dates back to the late 19th century. Early models were simple and had basic features. Over time, they evolved with technology. Modern upright bikes now have advanced features. These include digital screens and adjustable resistance.
Popularity In Fitness
Upright bikes gained popularity in the fitness world. They provide a low-impact workout. This makes them suitable for all fitness levels. Many people prefer them for indoor cycling. They are compact and easy to use. They also help in burning calories and building muscle strength.
Primary Muscles Targeted
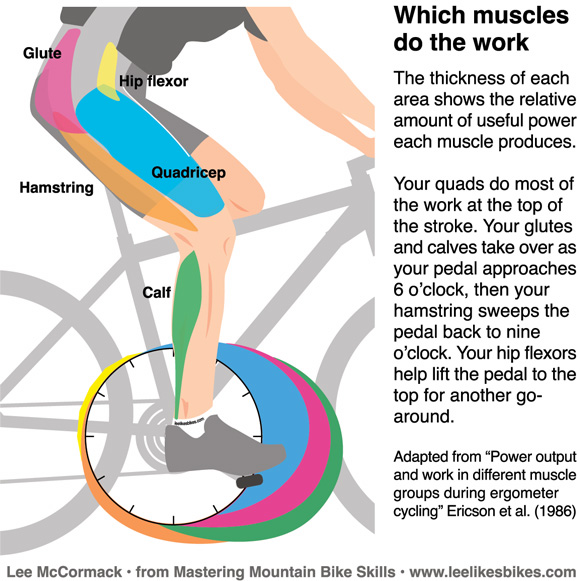
Riding an upright bike is a great way to work multiple muscle groups. The primary muscles targeted during an upright bike workout are the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. These muscles engage actively, providing a balanced lower body workout.
Quadriceps Activation
The quadriceps are the muscles on the front of your thighs. They play a crucial role during an upright bike workout. When you push down on the pedals, your quadriceps contract. This action helps to extend your knee and move the pedal downwards.
As you pedal faster, the quadriceps work harder. This results in increased muscle endurance and strength. For those seeking to tone their thighs, engaging the quadriceps is essential.
Hamstrings Engagement
The hamstrings are located at the back of your thighs. These muscles are essential for the pulling motion while cycling. As you pull the pedal upwards, the hamstrings contract. This action helps to flex the knee and lift the pedal.
Engaging the hamstrings helps balance the workout. It prevents muscle imbalance and promotes overall leg strength. Strong hamstrings support better cycling performance and reduce the risk of injury.
Secondary Muscles Involved
When using an upright bike, the primary focus is on the quadriceps and hamstrings. Yet, several secondary muscles get a decent workout too. These muscles play a vital role in stabilizing and supporting your body during the exercise.
Calves Contribution
The calves are crucial for pedaling. They engage with every push and pull. This movement helps in enhancing calf muscle strength.
Here are the main actions involved:
- Pushing down on the pedals
- Pulling up during the cycle
These actions help in toning the calf muscles. They also improve endurance and flexibility.
Gluteal Muscles
The gluteal muscles, or glutes, are vital for a balanced workout. They engage mainly during the downward push. This helps in strengthening the lower body.
Key benefits include:
- Improved posture
- Enhanced balance
- Better hip stability
Strong glutes also help in reducing lower back pain. They support the spine and enhance overall performance.
Core Stability And Strength
Riding an upright bike offers more than just a great cardio workout. It also plays a significant role in enhancing core stability and strength. A strong core is essential for overall fitness, balance, and posture. Here’s how the upright bike helps in building core stability and strength:
Abdominal Engagement
The upright bike requires you to maintain an upright posture, which naturally engages your abdominal muscles. Every pedal stroke you make forces your abs to contract and stabilize your body. This continuous engagement helps in toning and strengthening your abdominal muscles over time.
| Muscle Group | Role in Upright Bike Workout |
|---|---|
| Upper Abs | Helps maintain posture |
| Lower Abs | Stabilizes the lower body |
| Obliques | Aids in balance and side-to-side movements |
Lower Back Support
Core stability isn’t just about the front of your body. Your lower back muscles also play a crucial role. When you ride an upright bike, your lower back muscles work to keep your spine aligned and supported.
This not only helps in strengthening these muscles but also reduces the risk of lower back pain. A strong lower back is essential for overall core stability and a healthy spine.
- Erector Spinae: Supports the spine
- Multifidus: Provides stability to the vertebrae
- Quadratus Lumborum: Assists in lateral movements
Upper Body Benefits
Using an upright bike can enhance your upper body strength. While many think it only works the legs, it also benefits arm and shoulder muscles. Let’s explore how.
Arm Muscle Activation
When you grip the handlebars of an upright bike, your arm muscles engage. This includes the biceps and triceps. As you pedal, your arms help in maintaining balance and stability. This constant engagement strengthens your arms over time.
Consider the following:
- Gripping the handlebars tightens biceps.
- Maintaining posture activates triceps.
- Alternate hand positions to work different muscles.
Shoulder Involvement
Your shoulders play a crucial role while using the upright bike. They help in stabilizing your upper body. This continuous involvement ensures they stay engaged and toned.
Here’s how:
- Keeping your shoulders steady works the deltoid muscles.
- Posture maintenance activates shoulder blades.
- Proper grip spreads the load evenly.
To sum up, using an upright bike can be a full-body workout. It not only strengthens your legs but also engages your upper body, making it a comprehensive exercise option.
Credit: www.mtah.net
Cardiovascular Health
The upright bike targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. It strengthens the lower body while boosting cardiovascular health. Regular use enhances stamina and endurance.
Riding an upright bike isn’t just for toning muscles. It’s also great for your heart. This exercise gets your heart pumping and blood flowing. Let’s explore the benefits for cardiovascular health.
Heart Rate Improvement
Pedaling on the upright bike increases your heart rate. A higher heart rate means your heart works harder. This strengthens your heart over time. A strong heart pumps blood more efficiently. This can lower the risk of heart disease.
Endurance Boost
Consistent use of the upright bike can boost your endurance. As your cardiovascular system gets stronger, you can exercise longer without getting tired. This improves your overall stamina. Better endurance means you can handle daily activities with ease.
Comparing Upright Bikes To Other Equipment
When comparing upright bikes to other equipment, many wonder how they stack up. Understanding the differences can help you choose the best option for your fitness goals. This section dives into how upright bikes measure up against recumbent bikes and treadmills.
Versus Recumbent Bikes
Upright bikes and recumbent bikes both offer great cardio workouts. Yet, they target muscles differently. Upright bikes engage your core more. This happens because you must balance while pedaling. Your upper body also gets a slight workout. It’s because you lean forward and grip the handlebars. On the other hand, recumbent bikes focus more on your legs. You sit back in a reclined position. This position supports your back and reduces strain. Your glutes, hamstrings, and calves do most of the work.
Versus Treadmills
Treadmills provide a different kind of workout. They are excellent for building lower body strength and endurance. While running or walking, your leg muscles work intensely. This includes your quads, hamstrings, calves, and glutes. Upright bikes, however, offer a lower-impact option. They place less stress on your joints. This makes them ideal for those with knee or hip issues. Upright bikes still give your legs a good workout. Plus, they engage your core and upper body slightly.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Tips For Maximizing Benefits
Using an upright bike offers numerous benefits, including working various muscle groups. To maximize these benefits, follow these tips. Ensuring proper form, posture, and effective workout routines can help you achieve the best results.
Proper Form And Posture
Maintaining proper form and posture is essential for engaging the right muscles. Here are some key points:
- Keep your back straight: Avoid slouching or arching your back.
- Align your knees: Ensure your knees are in line with your feet.
- Grip the handlebars lightly: Avoid gripping too tightly to prevent shoulder strain.
- Adjust the seat height: Your leg should be almost straight when the pedal is at the lowest point.
Effective Workout Routines
Implementing effective workout routines can target specific muscle groups. Here are some routine suggestions:
| Routine | Muscles Targeted | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Steady-State Cycling | Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Glutes | Pedal at a consistent speed for 30 minutes. |
| Interval Training | Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Calves | Alternate between high and low intensity every 2 minutes for 20 minutes. |
| Hill Climbing | Glutes, Calves | Increase resistance to simulate climbing a hill for 15 minutes. |
For best results, combine these routines in your weekly workout plan. This will help engage different muscle groups and prevent workout monotony. Focus on consistency and progression to achieve your fitness goals.
Credit: www.bliese.my
Frequently Asked Questions
What Muscles Are Targeted By An Upright Bike?
The upright bike primarily targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. It also engages the core muscles for stability.
Does An Upright Bike Work The Upper Body?
While the upright bike mainly works the lower body, it also engages the core and can provide some upper body toning.
Is An Upright Bike Good For Abs?
Yes, riding an upright bike can help strengthen your core muscles, including the abs, by maintaining stability.
Does The Upright Bike Help Tone Legs?
Absolutely, the upright bike is excellent for toning the legs, especially the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves.
Conclusion
Upright bikes offer great workouts. They target various muscles. These include quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. Your core muscles also benefit. Regular use improves strength and endurance. It’s an effective way to stay fit. Plus, it’s easy on the joints.
Keep riding and enjoy the benefits. Happy cycling!


One response to “What Muscles Does the Upright Bike Work? Discover the Benefits”
[…] Bike tyres with puncture resistance are essential for avid cyclists. They provide a smoother, more reliable ride and reduce the risk of unexpected flats. These tyres are designed with special materials and technologies to withstand sharp objects and rough terrain. […]